Colour
What is colour?
It is quality such as red, blue, green, yellow, etc., that you see when you look at something.
The colour of something is the appearance that it has as a result of the way in which it reflects light.
Definition
Colour is the property possessed by an object that produces different sensations on the eye as a result of the way it reflects or emits light.
Objects appear to be different colours because of the difference in the colour wavelengths – which objects surface absorbs the wavelengths and reflect or transmit colours.
The colours we see are the wavelengths that are reflected or transmitted.
When describing the properties of something such as it’s big, small, long, short; another property we can describe is the colour of something.
Colour Glossary
Absorbed = Soak up
Aqua = A colour between Green and Blue
Blend / Mix = What you can do with colour to create another colour. For example, blending yellow and blue would create green.
Colour Blind = The inability of a person to correctly distinguish certain colors. Color vision problems range from the inability to see different shades of a color to not being able to see certain colors at all
Colour Scheme = A color scheme is the choice of colors used in various artistic and design contexts
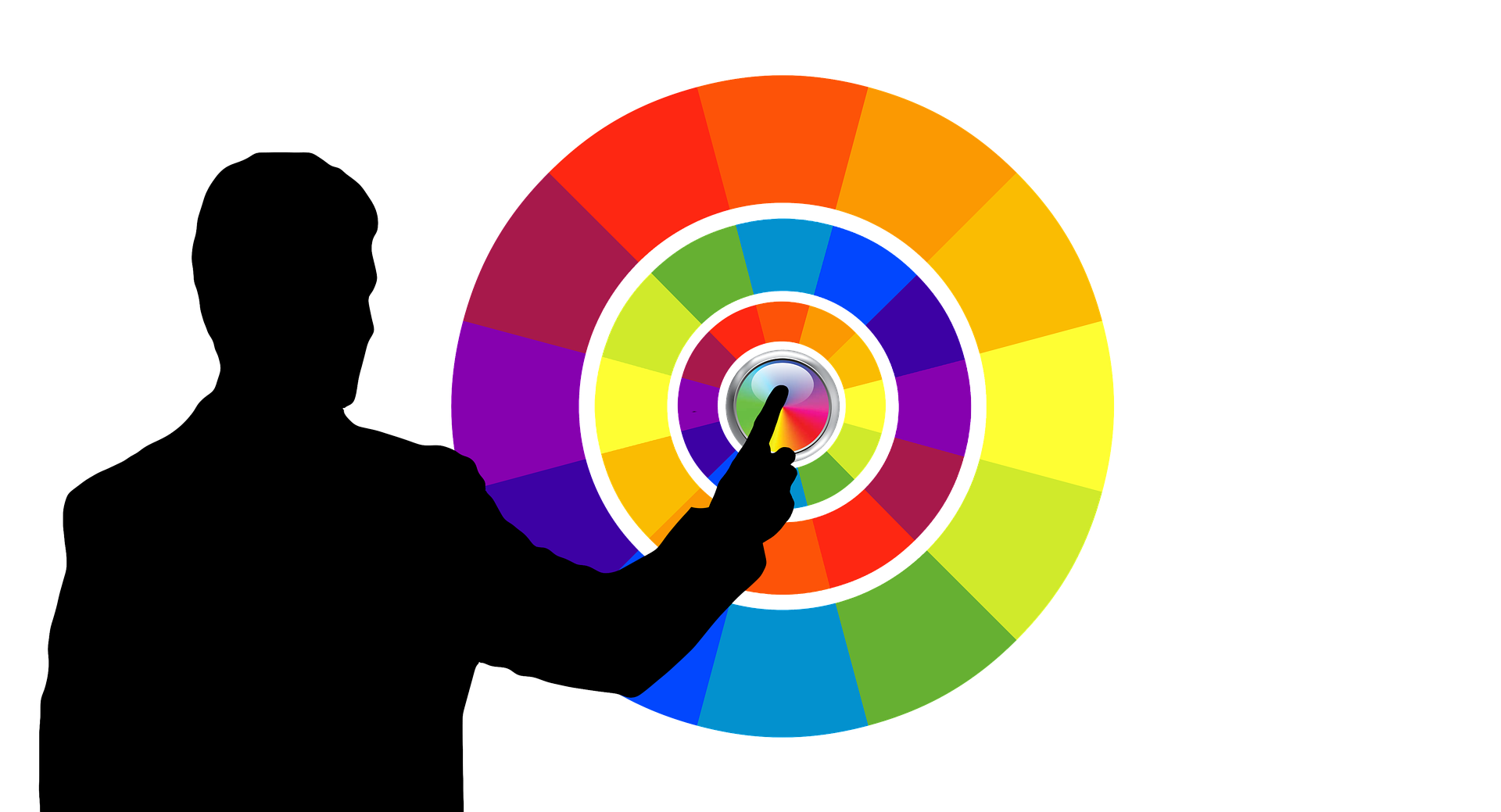
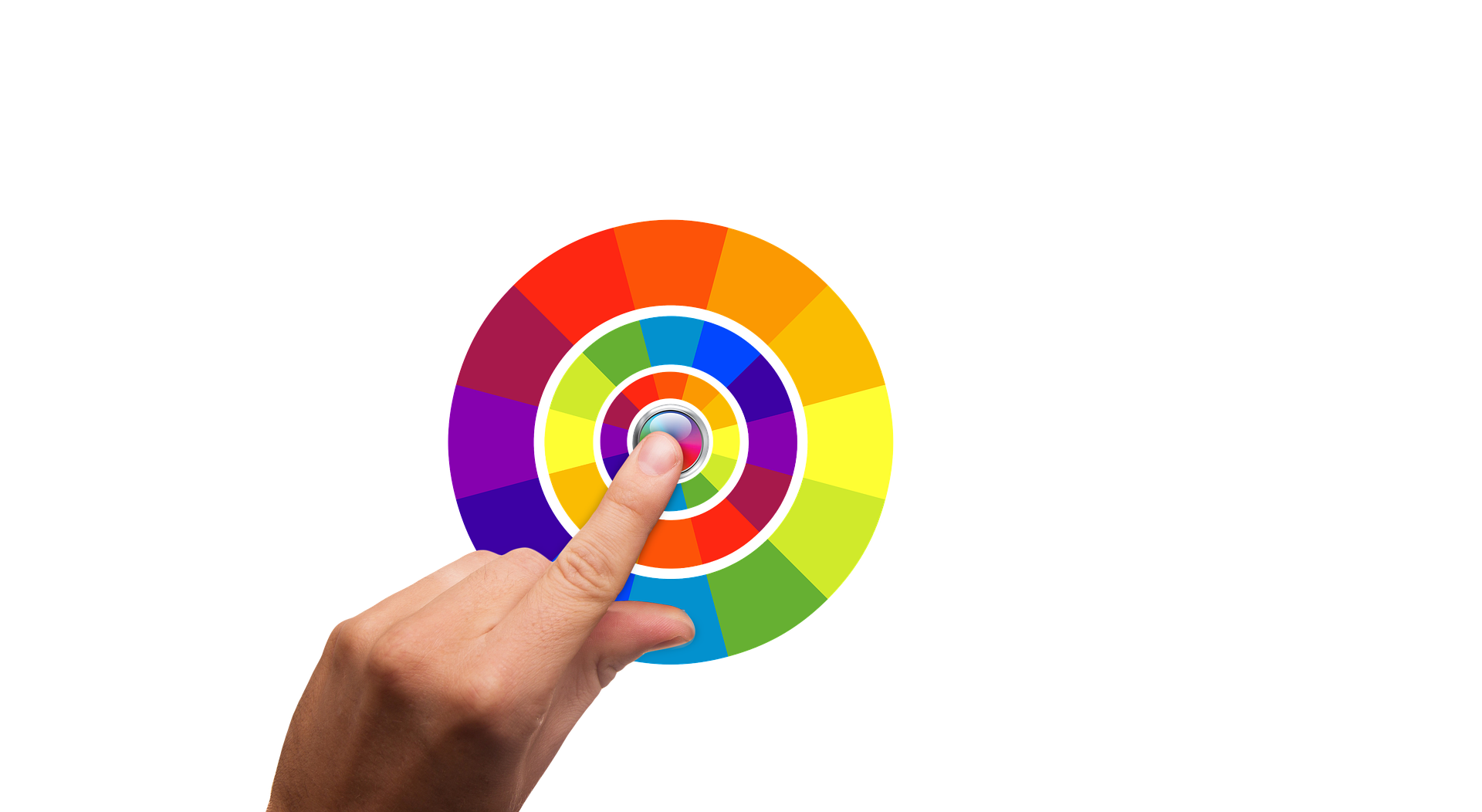
Colour Wheel = Is an abstract illustrative organization of color hues around a circle.
It shows the relationships between primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors
Contrast = Opposite
CMY = An abbreviation of cyan magenta yellow
Dichromats = They can only see two types of colour.
Dogs are dichromats.
Dye = If you dye something such as hair or cloth, you change its colour by soaking it in a coloured liquid.
Dyes are typically soluble at some stage in their use. Generally, dyes are often organic compounds.
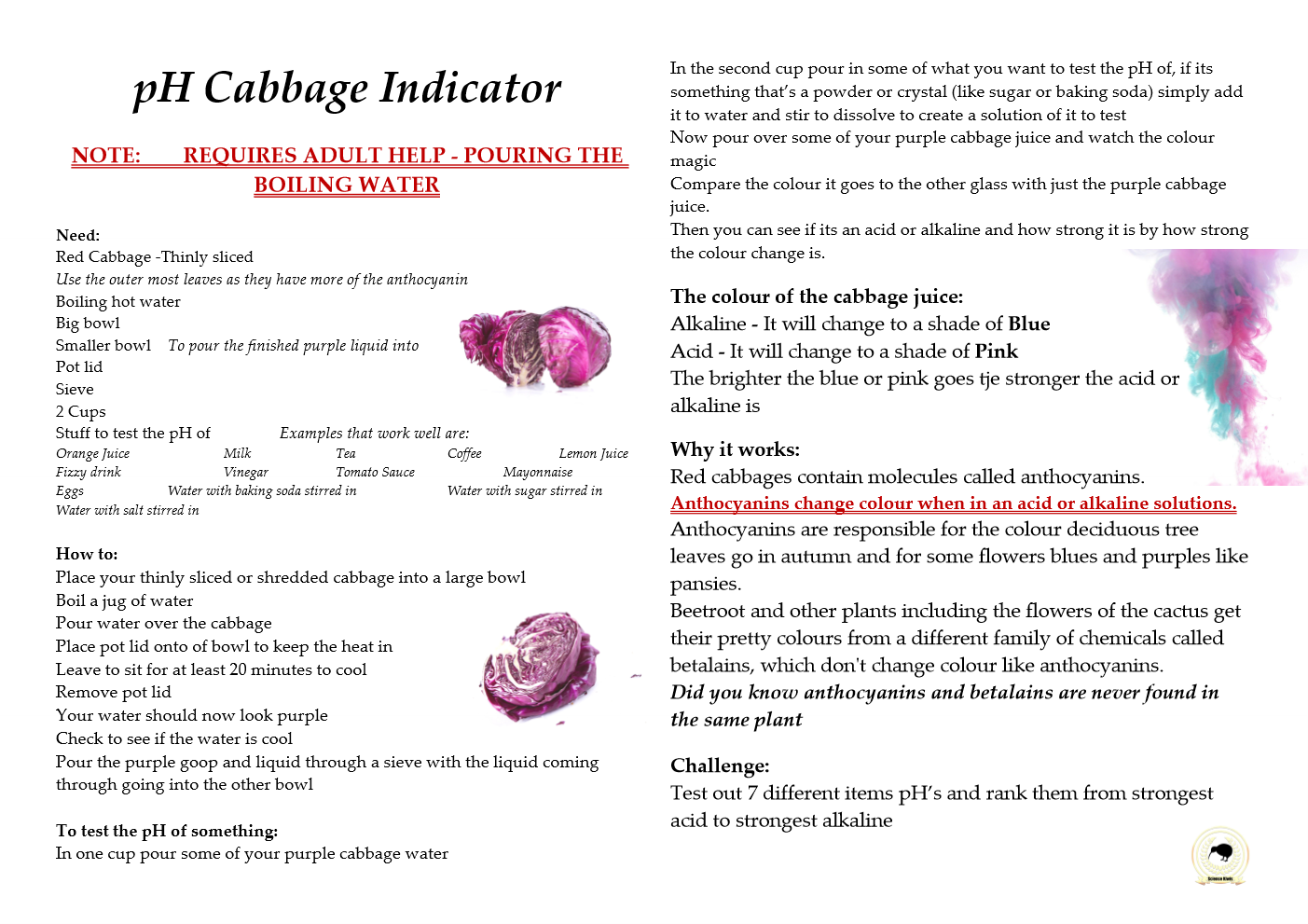
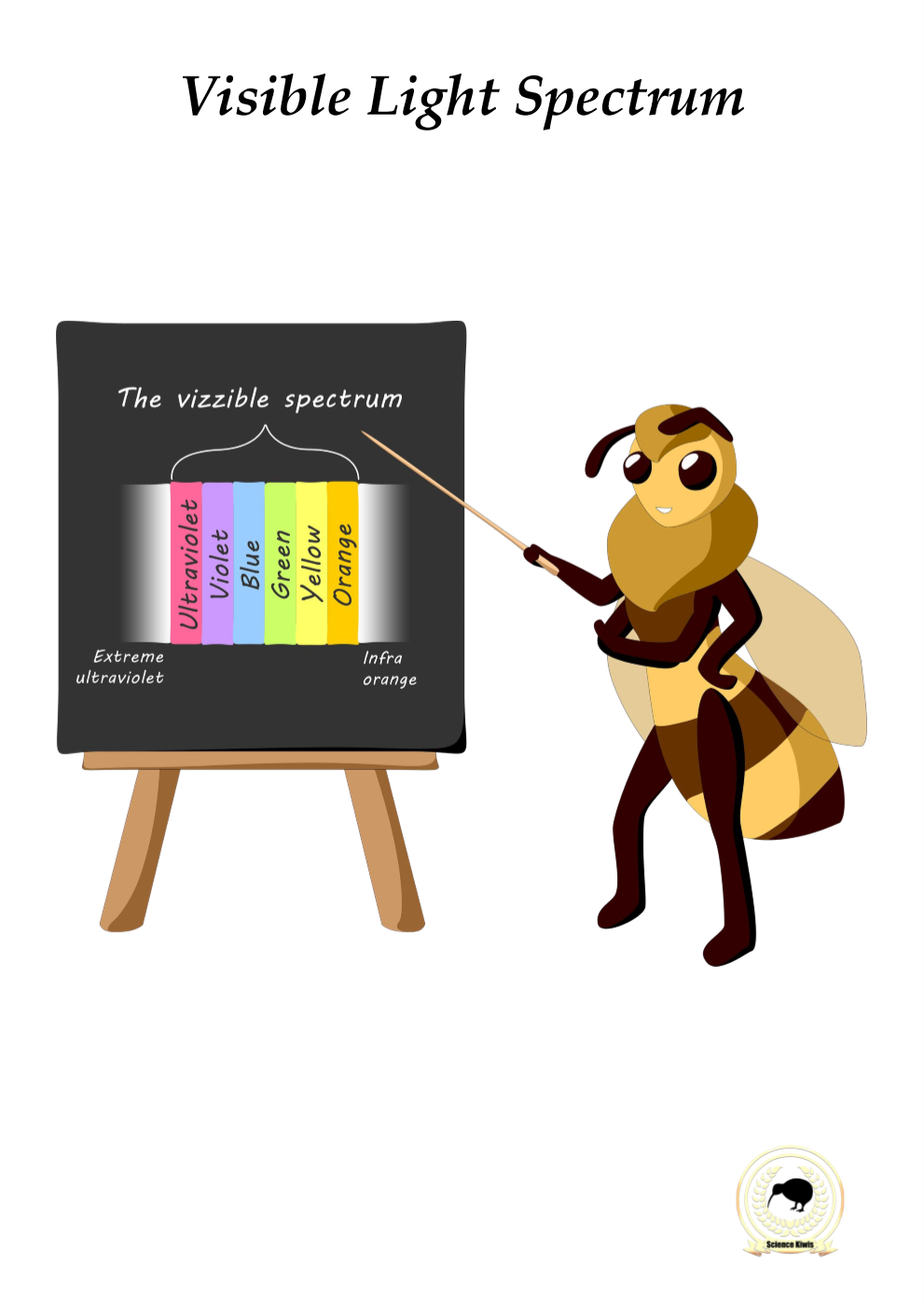
Electromagnetic spectrum
= The range of all light waves visible and invisible
Hue = The quality of a color as determined by its dominant wavelength
Indigo = Another name for purple
Lime = Another name for green
Neon = Neon colors are bright colors that appear to glow with intensity such as hot pink and electric blue
Paint = A coloured liquid coating that drys and coats a surface
Pastels = Pastels are pale light colour’s such as peach and lavender
Pigment = A pigment is a colored material that is completely or nearly insoluble in water.
Pigments are often inorganic compounds. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal
Primary colors = Red, yellow, and blue
RYB = An abbreviation of red yellow blue
Secondary Colors = Orange, green, and violet
Nuances = Colors of the same lightness and saturation, but of a different hue, are called nuances
Symbolism = The use of colour as a symbol to represent ideas, emotions, or qualities.
Tint / Shade = Any lighter or darker variation of a color
Colors of the same hue and saturation, but of different lightness, are called tints and shades.
Tone = Colors of the same hue and lightness, but of different saturation, are called tones.
Trichromats = Trichromatss have retinas that have three different kinds of cells that can receive color. Those cells are called cones.
Humans are trichromats.
Violet = Another name for purple
Did you know we need light to see different colours?
Next time you are in the dark have a look around, see if you can see the colours of the objects around you.
Colour is a very cool topic, it can be used across a variety of subjects and lessons, not just Art Class
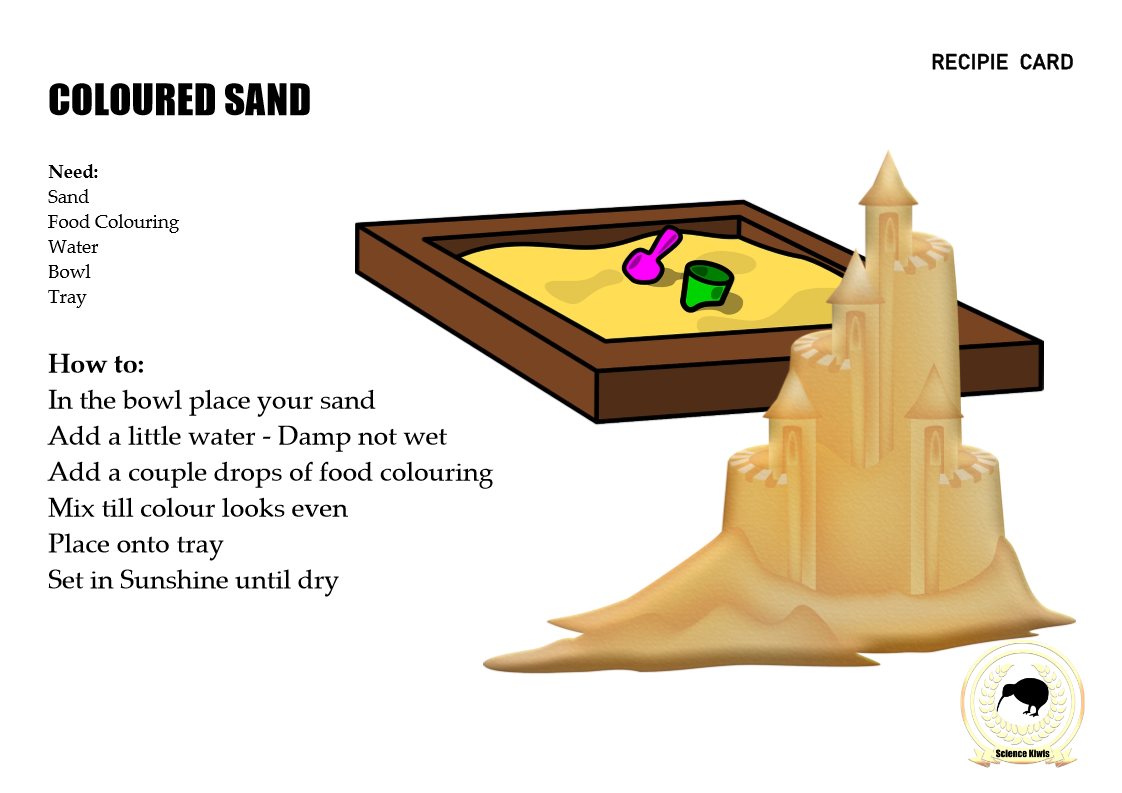
Colour experiments are great when learning about plants – colour changing flowers; the solar system – merry go round planets or solar system mobile; binary alphabet and binary coding – create the binary in coloured beads; sand is almost s subject entirely on its own – coloured sand is great to make; Learning about water, oil, mixtures, liquids? Try water fireworks for a beautiful display; Worried about the environment particularly the artic? – Try melting colour; For any subject or topic a great way to include multiple colours in an activity is to base it around many colours of playdough, modeling clay, foam, paper-mâché, moon sand, or even different colours of sherbet
When studying the topic of colour there are many components to consider:
There are the simple ones like naming and recognizing colours
There is understanding different shades of the same colour such as with blue, there are shades that are light like, sky blue, baby blue; shades that are bright like cobalt blue; shades that are dark like navy.
Along with looking at a colours tint, tone, and hue
The difference between primary and secondary colours
Colours in the visible spectrum of light
There are looking a pigmentation and how that affects colour produced
How to change the colour of things and how to mix colours to make new colours
Looking at issues of colours such as being colour blind
There is looking at natural and ancient methods of creating colours, such as paints and dyes
How colour affects emotion and also the symbolism of different colours
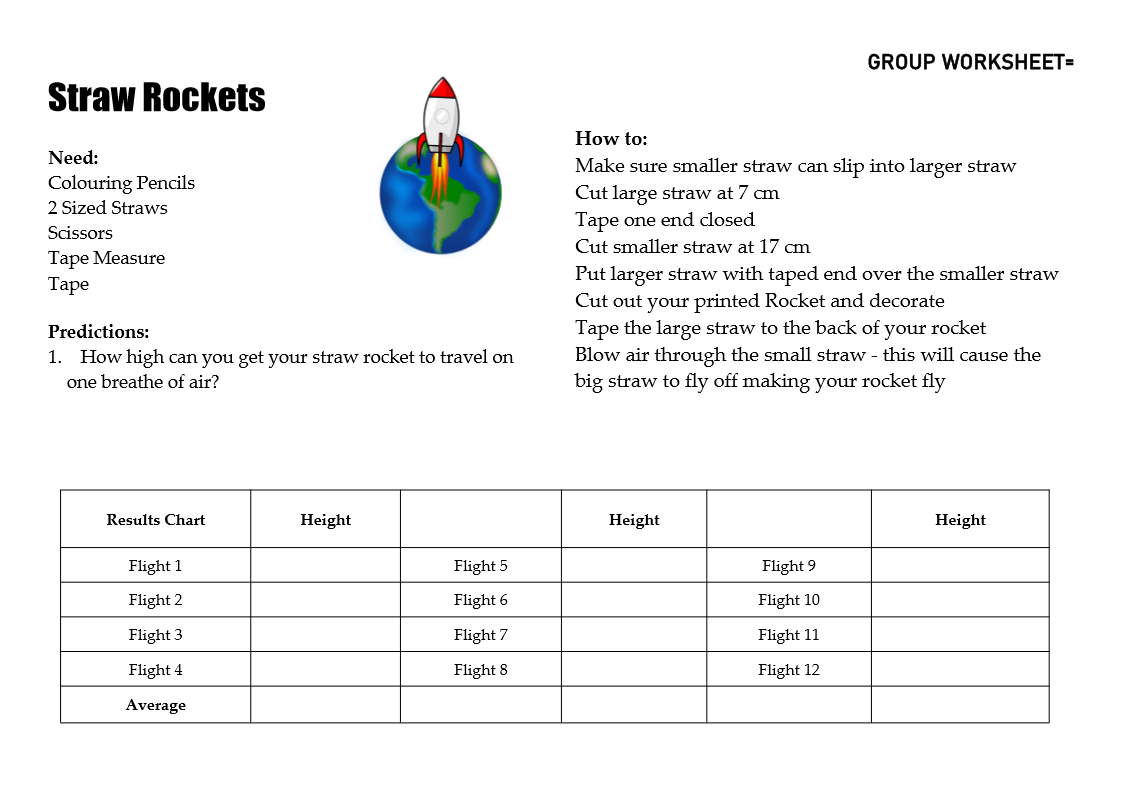
IMAGES :
To download / save / print – Simply right click and save the image.